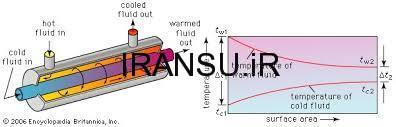
مبدل گرمایی با جریان ناهمسو
بر خلاف مبدل با جریان همسو ، در مبدل با جریان ناهمسو انتقال گرما بین قسمت های گرم دو سیال در یک سر ، و همچنین بین قسمت های سرد دو سیال در سر دیگر روی می دهد . به همین دلیل اختلاف دما ، در طول مبدل در هیچ جا به بزرگی ناحیه ورودی مبدل با جریان همسو نیست . توجه کنید که دمای خروجی سیال سرد در اینجا می تواند بزرگ تر از دمای خروجی سیال گرم باشد .
برای مبدل با جریان ناهمسو اختلاف دما در نقاط انتهایی به صورت زیر تعریف می شود :
\Delta {T_m}=\frac{\Delta T_1-\Delta T_2}{\ln \left( \frac{\Delta T_1}{\Delta T_2} \right) }
\Delta T_1=T_{h1}-T_{c2}
\Delta T_1=T_{h2}-T_{c1}
باید دانست که ، برای دماهای ورودی و خروجی یکسان ، اختلاف دمای میانگین لگاریتمی در جریان ناهمسو از اختلاف دمای میانگین لگاریتمی در جریان همسو بیشتر است . لذا ، با فرض مقدار U یکسان ، مساحت سطح لازم برای ایجاد آهنگ انتقال گرمای معین q در جریان ناهمسو کمتر از مساحت لازم در جریان همسو است . همچنین در جریان ناهمسو T_{c2} می تواند بیشتر T_{h2} از باشد ولی برای جریان همسو این طور نیست .
البته روشهای دیگری نیز برای تحلیل مبدل ها به کار می رود که در اینجا بیان نمی شود . از جمله روش NTU و روشهای تجربی .
Countercurrent flow heat exchanger
Unlike the parallel-flow exchanger, the heat transfer between the heat exchanger Countercurrent flow of fluid in one end, and the cold side of the fluid on the other end. Because of this temperature difference, the converter is nowhere as big as the input transducer is aligned with the flow. Note that the cold fluid outlet temperature here can be larger than the outlet temperature of the hot fluid.
Countercurrent flow for converting a temperature difference between the end points are defined as follows:
\ Delta {T_m} = \ frac {\ Delta T_1- \ Delta T_2} {\ ln \ left (\ frac {\ Delta T_1} {\ Delta T_2} \ right)}
\ Delta T_1 = T_ {h1} -T_ {c2}
\ Delta T_1 = T_ {h2} -T_ {c1}
It must be understood that, for the same inlet and outlet temperatures, the logarithmic mean temperature difference between the logarithmic mean temperature difference of the alignment of Countercurrent more. Thus, assuming the same U value, the surface area required for a given heat transfer rate q in Countercurrent flow in the line is less than the required area. Countercurrent during the T_ {h2} T_ {c2} can be greater than the current line, but it’s not.
However, other methods are used to analyze the converter is not described here. The NTU method and experimental methods.